Data Element
What is a Data Element?¶
A Data Element is a description of an individual field, variable, column or property of a data item. Each Data Element has a name and a Data Type.
How are Data Elements used?¶
Data Elements that are related to each other in some way are grouped together in Data Classes. These Data Classes are the building blocks of Data Models. For example, a Data Element could be an individual field such as ‘Postcode’ within a webform.
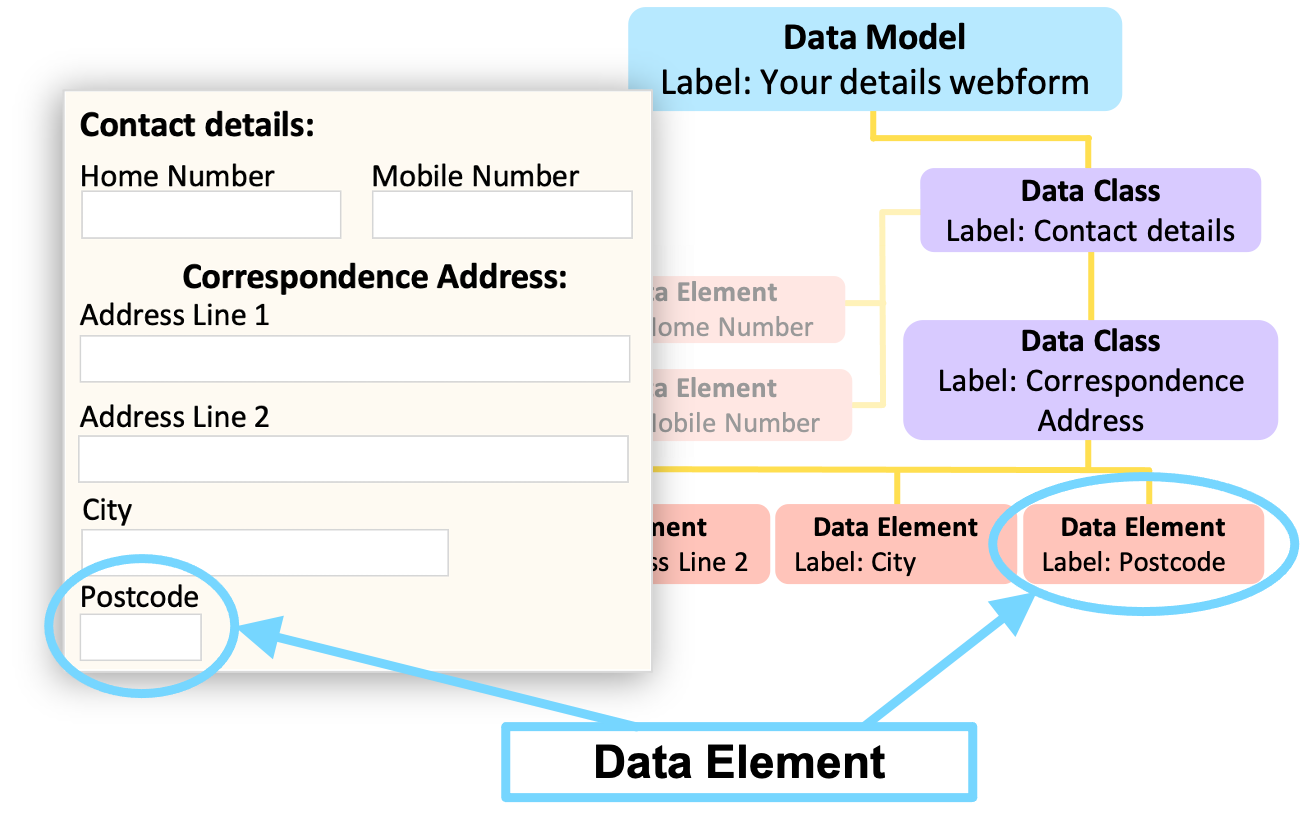
Each Data Element has a:
-
Label
This is the name of the Data Element which has to be unique within its parent Data Class. -
Aliases
Alternative names that can help locate the Data Element when searched for. -
Description
A definition either written in HTML, Markdown, or plain text which explains any contextual details relating to the Data Element. -
Data Type
The Data Type describes the range of possible values that the Data Element may take. The Data Types stored within Mauro Data Mapper are:-
Enumeration Data Type
This is a constrained set of possible Enumeration values, which are typically used to describe lists of data.
For example, an ethnicity Enumeration Data Type would include a list of different ethnic categories, each defined by a coded key and a human readable description. -
Primitive Data Type
Data without further details on structure or referencing. Primitive Data Types include ‘String’, ‘Integer’ or ‘Date’. -
Reference Data Type
Data which refers to another Data Class within the same Data Model. -
Terminology Data Type
A structured collection of Enumerated Values which have relationships between different data terms.
-
-
Parent Hierarchy
Details the parent Data Class and Data Model of the Data Element. -
Multiplicity
This specifies the minimum and maximum number of times the Data Element appears within its parent.
Optional data may have a minimum Multiplicity of 0 and a maximum of 1, whereas mandatory data has a minimum Multiplicity of 1. Data which occurs any number of times is given by a Multiplicity of '*' (which is represented by '-1' internally). -
Classifications
These are effectively tags that you can apply to the Data Element.
The above are all shown within the details panel, when the Data Element is selected in the Model Tree.
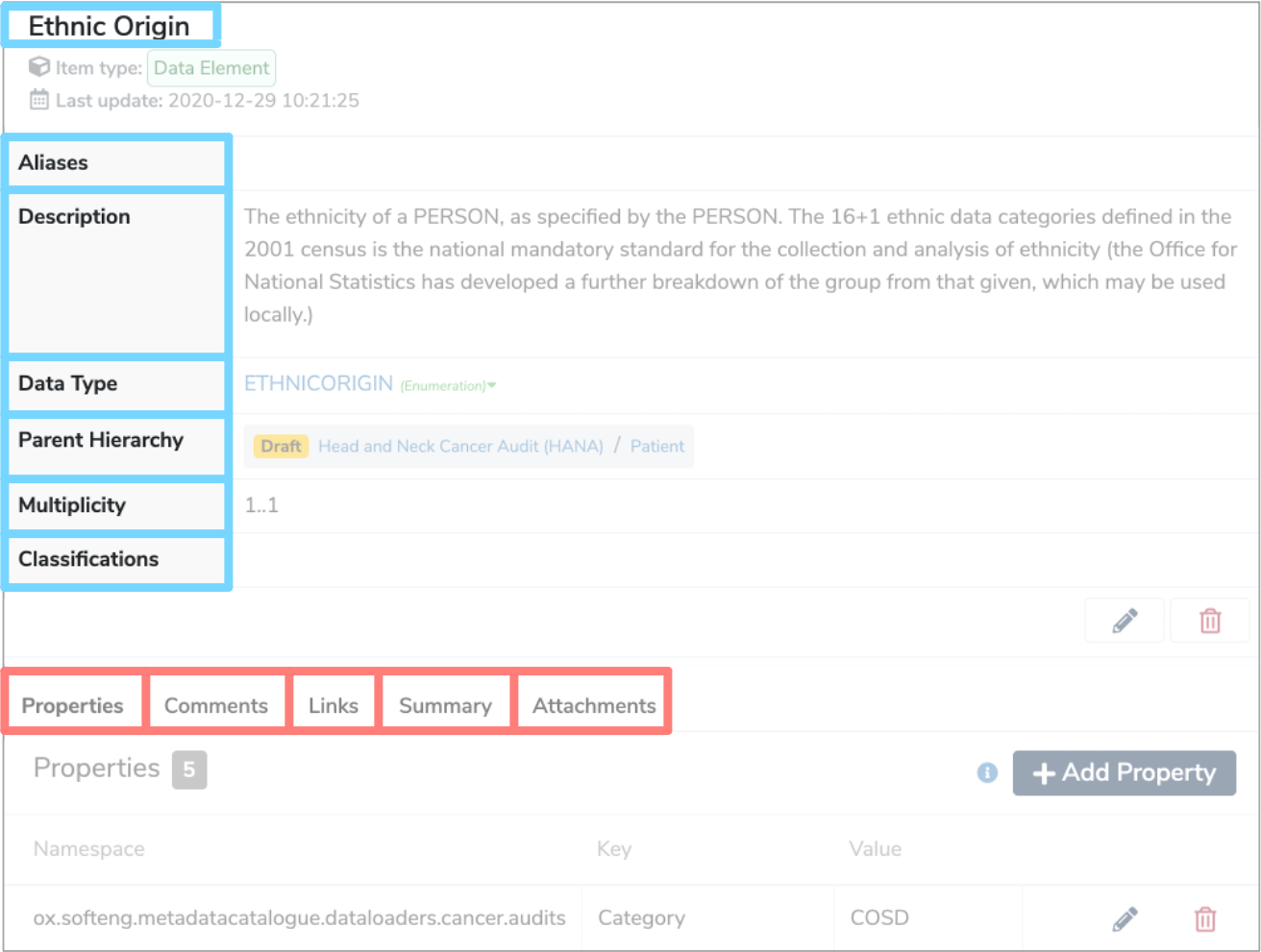
Other characteristics are displayed in the tabs underneath the details panel, when the Data Element is selected in the Model Tree.
-
Properties
Additional metadata about this Data Element. This can include technical information such as where the data is located, as well as information for users such as the type of data, coverage, geography and accessibility. -
Comments
Any relevant comments or notes. -
Links
Semantic links between relevant Data Elements. -
Summary
Further metadata information on the nature of the Data Elements. This can include aggregate data such as the number of entries or distribution information as well as textual information detailing aspects like the geographic representation of the data set or the duration of collection. -
Attachments
Files can be added to provide additional information and context.